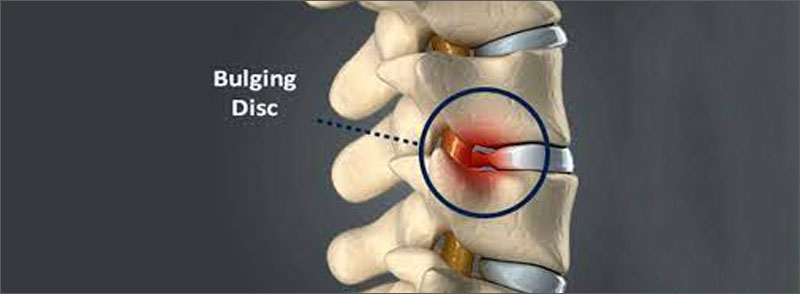
A bulging, or herniated, disk occurs when the spongy center of a disk in the spine pushes out through a tear in the outer, rubbery portion of the disk. It can press on the spinal cord and nerve roots, leading to pain and problems with mobility.
Bulging disks are usually due to age-related degeneration, while symptoms tend to progress gradually. People also call them herniated, ruptured, or protruding disks.
Doctors may recommend treatment for bulging disks in the back that range from short- to long-term options and that aim to decompress the spinal canal and ease the pain. This article examines the causes and symptoms of a bulging disk. It also looks at potential treatments and exercises that may offer pain relief.
What is a bulging disk?
A bulging disk occurs when the inner, jelly like portion of the disks between the bones in the spine bulge out through a tear in the outer (annulus) portion of the disk. A series of interlocking bones, called vertebrae, make up the spine. Between each vertebra is soft tissue, known as a spinal disk. The disks provide support for the spine and allow for movement between the vertebrae and to prevent bones from rubbing against each other. They also act as shock absorbers to prevent damage during movement. Each disk contains a tough outer layer with gel in the middle. This gel may lose its flexibility and become rigid with age. The amount of gel can also decrease with age, become compressed, and push out. When the disk bulges, it may compress or make contact with a nerve and trigger pain. Most bulging disks occur at the bottom of the lumbar spine. Sometimes, the outer layer of the disk breaks down and ruptures, and a gel-like center is pushed out through a tear in the disk’s exterior wall
Symptoms
Symptoms of a bulging disk depend on its severity and location in the spine.
Some people may have no initial symptoms. However, with further disk degeneration and herniation, a person may experience the following:
- back pain that worsens with movement, such as when sneezing
- spasms in the back muscles
- weakness and numbness in the legs and feet
- reduced mobility in the legs, knees, and ankles
- decreased bladder and bowel control
- difficulty walking
- sciatica
- reduced coordination
Pain may also radiate to different areas of the body, such as the arms or rib cage.
People should seek help at once if they experience a loss of bowel or bladder control. This can happen when a group of lumbar and sacral nerve roots become compressed. This is called cauda equina syndrome, which is a medical emergency.
Treatment
Treatments for a bulging disk will depend on its severity and location.
Doctors may recommend anti-inflammatory medications to help with pain and reduce inflammation. For people with severe pain, steroid injections may be a suitable short-term solution.
If the disk ruptures, bed rest may be necessary. Sometimes, if the condition is severe, a doctor may perform surgery to reduce pain and improve mobility.
